
Inspection | Electric Scooter Inspection Standards and Methods
General requirements for inspection of electric scooters
1. The electric scooter should not be dangerous under normal use, reasonably foreseeable misuse, or malfunction. Dangers include but are not limited to the following situations:
- The heat generated may cause material deterioration or personal burns;
- Hazards of burning, explosion, electric shock, etc.;
- During the charging process, toxic and harmful gases are released;
- Personal injury caused by breakage, deformation, loosening or motion interference of the vehicle or its components
2. The safety of lithium-ion batteries shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 40559, and the initial capacity, high-temperature capacity, and low-temperature capacity of the battery shall comply with the provisions of SJ/T 11685. Batteries that have been recycled shall not be used.
3. The safety of the charger should comply with the provisions of GB 4706.18 and should be compatible with the battery system of the electric scooter; the connector of the electric scooter charging port should be able to prevent misalignment and reverse insertion.
4 The combustion classification of circuit boards and non-metallic casings of batteries should not be lower than V-1 in GB/T 5169.1.
General requirements for inspection of electric scooters
Electric scooter inspection structure and appearance requirements
-Sharp edges: Use visual inspection and finger touch to check whether there are any parts of the rider's body that can touch the electric scooter. During normal riding, transportation and maintenance, there should be no exposed sharp edges on the rider's hands, legs and other parts of the body that may touch the electric scooter.
- Protrusions: The electric scooter is in an upright position. Visually inspect the handlebar end: Use a vernier caliper to measure the length of the bolt end after assembly. The rigid protrusions of the electric scooter should meet the following requirements:
● For rigid protrusions that may injure the rider, the ends of the protrusions should be protected with protective materials of appropriate shapes (e.g. silicone or rubber protective sleeves on the ends of the handlebar);
● For bolts, the length of the part beyond the thread fitting is less than the nominal diameter of the bolt.
- Clearance: Use a go/no-go gauge to measure the clearance of the electric scooter. Excluding the wheels (the clearance between the wheels and their support system, and between the wheels and fenders), the suspension system, the braking system, the brake handles, and the folding mechanism, the clearance of the electric scooter should be less than 5 mm or greater than 18 mm.
-Internal wiring: Use visual inspection to check the internal wiring of the electric scooter. The internal wiring should meet the following requirements:
● The wires are firmly fixed, not under excessive pressure, and not loose. Two or more wires with the same direction are bundled together; the wires are placed on parts without sharp corners or sharp edges; Note: Excessive pressure refers to pressure that causes obvious deformation of the wire.
● There is an insulating sleeve at the wire connection;
● When the wire passes through a metal hole, the wire or the metal hole is equipped with an insulating sleeve component.
Electric scooter inspection performance requirements
1. Maximum speed
The inspector drives the test vehicle from a standstill, accelerating it while holding the throttle at full speed until it reaches and maintains its maximum speed. The inspector then drives the vehicle through a 5-meter test section, recording the speed over that section. The test is repeated twice, and the average value is taken. The maximum speed of an electric scooter should be within ±10% of the manufacturer's stated maximum speed and should not exceed 25 km/h.
2. Motor start
Connect a DC ammeter in series to the test vehicle's motor input. When the test vehicle's speed is below 3 km/h, adjust the speed knob to its maximum setting and check the ammeter reading to verify the motor's operation. Increase the test vehicle's speed to above 3 km/h, use electric driving, and then apply the brakes. After the test vehicle's speed drops to between 1 km/h and 3 km/h, adjust the speed knob to its maximum setting again and check the ammeter reading to verify the motor's operation. When the electric scooter's speed is below 3 km/h, its motor should not output power.
3. Braking performance
Use visual inspection to check the braking system of the test vehicle. The electric scooter should have two or more (including two) braking systems, and at least one should be a mechanical braking system. 5.2.4.2 Fully exerted average deceleration. When all braking systems are used, the fully exerted average deceleration should be ≥3.4 m/s; when only the mechanical braking system is used, the fully exerted average deceleration should be >2.5 m/s.
Electrical safety inspection for electric scooters
1. Maximum output voltage
Fully charge the battery and let it sit for 2 hours. Measure the voltage with a DC voltmeter. The maximum output voltage of the battery should be less than or equal to 60 V.
2. Short-circuit protection
Check the test vehicle's battery charging and output circuits against the circuit diagram to see if they are equipped with protective devices such as fuses. If necessary, check the charging circuit, battery output circuit, or circuit board. Both the charging and battery output circuits of the electric scooter should be equipped with protective devices such as fuses.
3. Insulation resistance
The insulation resistance between the power circuit, control circuit and exposed conductive parts of the electric scooter should be greater than 2mΩ.
4. Fever
Secure the test vehicle to the test bench and apply the manufacturer's maximum load until the low battery warning appears. Measure the temperature of the handlebar grips, pedals, exposed cables, and connectors. Visually inspect any surface temperatures exceeding 57°C and any protective measures in areas easily accessible to the rider. Check for high-temperature warning signs prominently marked on areas such as the motor and brake system.
The heating of electric scooters should meet the following requirements:
During the test, the surface temperature of the parts that the rider is in continuous contact with (such as handlebars, pedals, etc.) shall not exceed 43°C; for brake systems with an operating temperature greater than 60°C, warning signs shall be marked on the exposed parts or in obvious places around them;
During the test, except for the braking system, the surface temperature of parts that are easily touched by riders (such as cables, connectors, etc.) shall not exceed 57°C; if there are parts with a surface temperature greater than 57°C, protective measures shall be taken.
5. Charging lock
Use an adapter charger to charge the battery of the test vehicle that is turned off. Turn on the power switch during the battery charging process and check the operation of the test vehicle's motor. During the battery charging process, the electric scooter's motor should not be running.
6. Brake power off
Electric scooters should have a brake power-off function. When braking, the motor input current should be less than or equal to the current when it has no torque output (standby current) within 3 seconds.
7. Charging port protection
Check the charging port on the test vehicle to see if reverse polarity protection is effective. Check that the test vehicle's charging port and the charger's output port are the only connection method. If not, try connecting the charger in reverse. The charging port on an electric scooter should have reverse polarity and electric shock protection features.
Electric scooter inspection and mechanical safety inspection
1. Pedal static strength
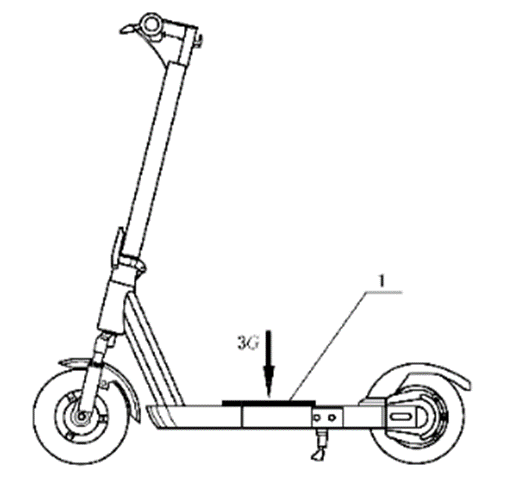
Apply a load (G) three times the manufacturer's specified maximum load at the center of the pedal using a support with a cross-sectional size of 150 mm x 150 mm. Maintain the load for 5 minutes. Remove the load, allow the pedal to rest for 10 minutes, and measure the permanent deformation of the pedal at the load-bearing location. The permanent deformation of the pedal at the load-bearing location of an electric scooter should not exceed 5 mm.
2. The entire vehicle load falls
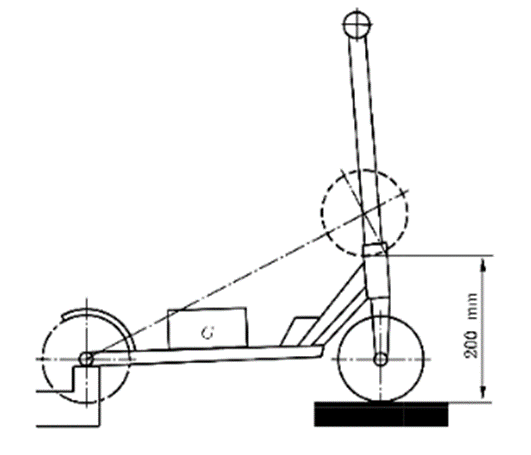
Apply and fix the maximum load (G) specified by the manufacturer to the test vehicle's pedals. Fix the rear wheels, raise the front wheels, and when the front wheels are 200 mm above the test surface, drop the vehicle onto a flat surface of a hard or similar hardness, as shown in the figure. Repeat the drop three times.
After the test, the electric scooter should not catch fire, explode, or leak fluid, its main load-bearing structure should have no obvious damage or deformation, and it should drive normally.
3. Pull-off force
The end of the handlebar tube should be equipped with a grip or handle cover that can withstand a pull-out force of 70 N. For quick-release handlebar tubes, after assembling the quick-release part and the handlebar tube, apply force along the quick-release direction of the handlebar tube. The quick-release part and the handlebar tube should not separate.
4. Static load strength of handlebar
Carry out the handlebar strength test in the following manner
- Downward force resistance: Fix the test vehicle horizontally so that it remains vertical during the test. Simultaneously, apply a vertical load of (250 ± 5) N to the middle of the two grips and maintain this load for 5 minutes.
- Upward force resistance: Fix the test vehicle upside down and simultaneously apply a vertical load of (250 ± 5) N to the middle of the two handles and maintain for 5 minutes.
- Forward force resistance: Fix the test vehicle horizontally so that it remains vertical during the test. Simultaneously apply a forward load of (250 ± 5) N to the middle of each grip and maintain this load for 5 min.
- Anti-rearward force: Fix the test vehicle horizontally so that it remains vertical during the test. Simultaneously, apply a backward load of (250 ± 5) N to the middle of the two handles and maintain it for 5 minutes.
After the test, visually inspect the handlebars and locking devices. The handlebars should not have obvious deformation; the handlebars and their locking devices should not have cracks or breaks, and should operate and lock normally.
5. Handlebar fatigue strength
Secure the test vehicle horizontally so that it cannot move and the handlebars cannot rotate. Apply a force of 270 N in the upper rear direction (upper/rear), at a 45° angle to the vertical, evenly distributed on both sides of the handlebar tube, 25 mm from the end. Repeat the operation in the opposite direction (lower/forward). Applying force in both directions constitutes one cycle. Repeat 10,000 cycles at a frequency no greater than 1 Hz. After the test, visually inspect the handlebars. No visible cracks, damage, deformation, or looseness should be present.
6. Steering fatigue strength
Secure the test vehicle horizontally so that the vehicle body cannot move, but the handlebars and front wheel can rotate freely about their axes. Apply a torque of 10 N·m and rotate the handlebars from one extreme position to the other, repeating this cycle 10,000 times at a frequency no greater than 0.5 Hz. After the test, the handlebars, flexible wires, and their sheaths must show no visible cracks, damage, significant deformation, or looseness.
7. Vehicle vibration
After the test, the battery of the electric scooter should not catch fire, explode, or leak, any part of the mechanical structure should not have cracks or breaks, and all electrical components should function normally.
8. Vehicle fatigue strength
Place and secure the manufacturer's maximum load at the center of the test vehicle's pedals. Apply a 5 kg load to the center of each grip. Secure the rear wheel of the electric scooter and place the front wheel on a roller with a diameter of at least 700 mm. Evenly install three 5 mm high bosses (20 mm top width, 17° in the uphill direction and 45° in the downhill direction) on the roller surface. Travel the roller at a speed of 2 m/s for 50 km. After the test, visually inspect all parts of the test vehicle for any abnormalities. When testing a multi-track test vehicle, stagger the bosses to prevent two or more wheels from passing over them simultaneously.
After the test, the electric scooter should meet the following requirements:
- There are no visible cracks, breaks or separations in any part of the frame;
- If a gap occurs, it will not affect the operation of the components and the safety of the user.
Electric scooter inspection and component inspection
1. Folding locking device
The requirements for the folding locking device are as follows.
- The folding locking device should require two consecutive operations to open, and the second operation depends on the rider performing and maintaining the first operation to be effective (such as a safety lock).
- The locking device should clearly indicate whether the device is in the released or locked position.
- When the folding locking device is locked, it should not be accidentally released or unlocked while riding. When a force of 150N or a torque of 2.2N·m is applied in the direction in which the folding locking device is most likely to be opened by a single operation, it should not break or be permanently deformed.
- The folding locking device should not break or permanently deform when subjected to a locking force of 250 N.
- The folding locking device should not touch moving parts while riding.
2. Telescopic mechanism
Use test gauges and pressure gauges to check the structure, clearance, and displacement of the telescopic mechanism. The telescopic mechanism should meet the following requirements:
- Each telescopic mechanism has a locking device;
- The gap between the telescopic mechanism and the locking mechanism is no more than 5 mm;
-After the telescopic mechanism is locked, a force of 250 N is applied along the telescopic direction for 1 min, and there is no relative displacement.
3. Pedals
Use a length measuring instrument to measure the anti-slip area of the test vehicle's pedal. The anti-slip area of the electric scooter's pedal should not be less than 150 cm.
4. Battery
Connect a DC regulated power supply to the test vehicle and turn it on to check the motor's operation. The electric scooter should be powered by original batteries. Original batteries are batteries manufactured by other manufacturers with authorization or permission from the original electric scooter manufacturer.
5. Wheels
Use universal measuring tools to measure the outer diameter of the wheels and the width of the tires of the test vehicle. All wheel sizes of electric scooters should meet the following requirements
- Wheel outer diameter 2125 mm;
- Tire width > 25 mm.
6. Warning device
Visually inspect the test vehicle's lighting, reflectors, or light signaling devices. Electric scooters should be equipped with a lighting device at the front and reflectors at the front, rear, and left and right sides. Electric scooters should also be equipped with a horn. The sound pressure level of the horn should be between 75 dB(A) and 95 dB(A).
7. Master switch
Electric scooters should be equipped with a main control device that is obvious, easy to access and not easy to operate incorrectly to turn on and off the driving power, and the device should be triggered by the rider's autonomous behavior.
Other inspection points for electric scooters
1. Instructions
- The instruction manual of the electric scooter should include relevant instructions and usage information on the use, operation and maintenance of the electric scooter, including at least the following contents.
● Security and restrictions:
● The use of this product must comply with relevant laws, policies and other information
● Information on protective measures taken by users when wearing helmets, knee pads, elbow pads and other protective gear;
● Detailed description of the operation, storage and charging of the electric scooter, including but not limited to environmental conditions, road conditions, etc.;
● Description of the operating environment and potential risks that may cause dangerous situations when the electric scooter is used and driven, and warnings about the risk of high temperature burns;
● Restrictive information such as user age and physical condition
-Product parameters and usage:
● The size and mass of the electric scooter, as well as the load or load capacity restrictions; the protection level of the electric scooter's casing;
● How to charge an electric scooter:
● The location and specifications of the electric scooter's fuse and other protective devices, as well as their markings on the simplified circuit diagram;
● How to store and use electric scooters;
● Electric scooter range and its test methods and conditions
-Maintenance:
Maintenance information for electric scooters, as well as information prohibiting users from disassembling and repairing them without authorization
- Additional Information:
-Product implementation standards;
-After-sales service contact information such as service phone number or email address:
-Other safety warnings.
2. Logo
-Product logo
The product label of an electric scooter should include necessary information to inform users and its specifications, including at least the following information:
● Product name and model;
● Manufacturer’s name or trademark, manufacturer’s address;
● Maximum output voltage;
● Maximum load;
● Maximum speed
-Safety warning signs
The electric scooter body should have necessary safety warning signs to inform users of safe use. When necessary, safety warning signs should be provided for precautionary measures when using, operating, and maintaining the electric scooter. Safety warning signs include but are not limited to:
● Warnings and signs for hot parts;

● Mark indicating the locking position of the safety lock of the folding locking device;
● The logo of the charging port of the electric scooter;
● Electric scooters are prominently marked with warning signs such as "Use only original chargers"
● Read the warning information or icons in the instruction manual before use
-Packaging logo
The product packaging should have the following logo:
● Manufacturer’s name and trademark;
● Product name;
● Model;
● Standard number (can also be marked on the product or instruction manual);
● Box size (length x width x height) and volume;
● quantity;
● Storage and transportation signs such as "Handle with care" and "Keep away from moisture";
● Production date or batch number.
3. Packaging
-Products leaving the factory should be accompanied by product certificates, packing lists, and product descriptions.
- External cartons or other packaging boxes should be tied securely.
Share this product

Inspection | Electric Scooter Inspection Standards and Methods
Standard specification: GB/T 42825-2023 General technical specification for electric scooters It specifies the structure, performance, electrical safety, mechanical safety, components, environmental adaptability, inspection rules and marking, instructions, packaging, transportation and storage requirements of electric scooters, describes the corresponding test methods, and defines the corresponding terms and definitions.
